Kadanes Algorithm
25 Dec 2020 - Hadron DaVinci
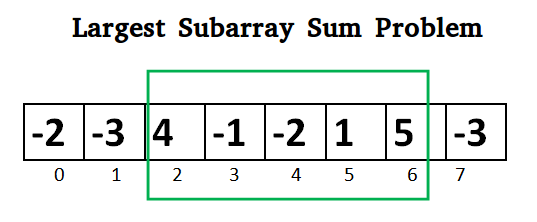
Kadane’s algorithm can be used to find the max sum in any contiguous
subarray.
Examples
kadane([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]) == 7
kadane([2, -1, -2, 1, -4, 2, 8]) == 10
kadane([-1, -1, -1]) == -1
Methods
Method 1
Time Complexity: O(N)
Spatial Complexity: O(1)
Method 1 Summary
The idea here is to loop through each number in the array and keep track of a running total.
Once the running total becomes negative, since we’re trying to find the maximum,
(it is not advantageous to hold on to that negative value), reset the running total as the current number.
- Initialize variables
- set
best_sumat negative Infinity.
- We do this b/c we’re going to maximize
best_sum- set
running_totalat Zero- Loop through each number:
- When
running_totalis negative:
- set
running_totalto Zero.
this represents the start of a new sub array sum- add
this_numbertorunning_total- Set
best_maxas the maximum of (best_maxand the currentrunning_total)
- if
best_maxactually does get updated,
that represents the end of a subarray- Return
best_max
Method 1 Solution
def kadane(arr: list) -> int: best_sum = float('-inf') running_total = 0for this_number in arr: if running_total < 0: running_total = 0running_total += this_numberbest_sum = max(best_sum, running_total) return best_sum
# Try Code if __name__ == "__main__": assert kadane([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]) == 7 assert kadane([2, -1, -2, 1, -4, 2, 8]) == 10 assert kadane([-1, -1, -1]) == -1
Method 2
Time Complexity: O(N)
Spatial Complexity: O(1)
Method 2 Summary
This method is really the same as method1. The only difference is that logic
for settingrunning_totalhas been consolidated to one line.
Personally, I prefer method1 since method2 obscures some of the logic
being used.
- Initialize variables
- set
best_sumat negative Infinity.
- We do this b/c we’re going to maximize
best_sum- set
running_totalat Zero- Loop through each number:
- Set
running_totalas the maximum of (this_numberand (running_total+this_number))
- This is a shorthand way of saying:
Ifrunning_totalis less than 0, then setrunning_totalequal tothis_number- Set
best_maxas the maximum of (best_maxand the currentrunning_total)- Return
best_max
Method 2 Solution
def kadane(arr: list) -> int: best_sum = float('-inf') running_total = 0for this_number in arr: running_total = max(this_number, running_total + this_number) best_sum = max(best_sum, running_total) return best_sum
# Try Code if __name__ == "__main__": assert kadane([-2, -3, 4, -1, -2, 1, 5, -3]) == 7 assert kadane([2, -1, -2, 1, -4, 2, 8]) == 10 assert kadane([-1, -1, -1]) == -1